If you want to make your website easy to navigate and connect your visitors to important pages, knowing the right HTML code for a link is a must. You might think adding links is tricky, but it’s simpler than you imagine.
By learning just a few simple steps, you can create clickable links that guide your audience exactly where you want them to go. Keep reading, and you’ll discover how to write clean, effective HTML links that make your site more user-friendly and professional.
Your visitors will thank you, and you’ll feel confident managing your own web pages.
Basics Of Html Links
HTML links connect web pages and help users navigate the internet. They allow visitors to jump from one page to another. Understanding the basics of HTML links is important for any web developer. Links make websites interactive and useful.
Creating links in HTML is simple. It uses a special tag called the anchor tag. This tag tells the browser where to go when the link is clicked. Knowing how to write and use this tag is the first step.
A Anchor Tag Syntax
The anchor tag is written as in HTML. It wraps around the text or image that becomes clickable. The basic form looks like this:
Link TextThe href attribute inside the tag sets the destination address. The text between the tags shows as the clickable link on the page.
A Essential Attributes
The href attribute is the most important part of the anchor tag. It defines the URL to open when the link is clicked. Without href, the tag won’t work as a link.
Other useful attributes include target. This controls how the link opens. For example, target="_blank" opens the link in a new tab.
The title attribute adds extra info. It shows a tooltip when users hover over the link. This helps users understand the link’s purpose.
Types Of Links
Links connect pages and websites. They help users navigate and find content easily. Different types of links serve different purposes. Understanding each type helps you build better web pages.
Internal Links
Internal links connect one page to another on the same website. They guide visitors to related content within your site. These links improve site structure and user experience. They also help search engines find and index pages.
External Links
External links point to pages on other websites. They provide additional information or sources. These links build trust and credibility. Use them to support your content with useful references.
Anchor Links
Anchor links jump to a specific part of the same page. They help users quickly find important sections. These links improve page navigation, especially on long pages. They use an ID attribute to mark the target spot.
Email Links
Email links open the user’s email program to send a message. They use the mailto: protocol in the link’s code. These links make it easy for visitors to contact you. Use them for customer support or inquiries.
Styling Links
Styling links makes your webpage look neat and clear. Links are important for navigation. Good styles help users see where to click. You can change colors, fonts, and effects. These small changes improve user experience. Below are common ways to style links using HTML and CSS.
Default Styles
Browsers add default styles to links. Usually, links are blue and underlined. Visited links change color to purple. These styles show users which text is clickable. Default styles work well but look plain. You can keep them or customize for your site.
Custom Colors And Fonts
Change link colors to match your design. Use CSS code like color: red; to set a new color. Fonts can also change to fit your style. Use font-family to pick a font. Custom styles make links stand out. Pick colors that are easy to read on your background.
Hover And Active Effects
Hover effects show when users move the mouse over links. Use CSS like :hover to change color or add underline. Active effects show when users click a link. Use :active to style the link during click. These effects give feedback and improve interaction. Simple animations can also make links feel alive.

Credit: www.wikihow.com
Advanced Link Features
Advanced link features help improve user experience and website performance. These features make links more useful and safer. They also help search engines understand your content better. Using these features correctly can boost your site’s SEO and accessibility.
Open Links In New Tabs
Sometimes, you want a link to open in a new browser tab. This keeps visitors on your page while they check the link. Use the target="_blank" attribute inside the tag. It looks like this:
Visit ExampleThis command opens the linked page in a new tab or window. It helps users stay on your site longer.
Adding Titles For Accessibility
Screen readers use the title attribute to describe links. Adding a title helps users with disabilities understand the link’s purpose. The title shows as a tooltip when users hover over the link. Use it like this:
ExampleAlways keep titles clear and simple. This improves accessibility and user experience.
Using Rel Attributes
The rel attribute defines the relationship between your page and the linked page. It adds security and SEO benefits. Common values include nofollow, noopener, and noreferrer. Example:
Examplenoopener and noreferrer protect against security risks. nofollow tells search engines not to follow the link. Use rel wisely to protect your site and improve SEO.
Common Link Issues
Links are a key part of any website. They guide visitors to other pages and resources. But links can have problems that hurt user experience and site ranking. Understanding common link issues helps keep your site healthy and user-friendly.
Broken Links
Broken links point to pages that no longer exist. Visitors see error messages or blank pages. This frustrates users and lowers trust in your site. Search engines also penalize sites with many broken links. Regularly check your links and fix or remove broken ones.
Seo Considerations
Links affect how search engines view your site. Use clear and relevant link text. Avoid generic phrases like ”click here.” Proper links improve site ranking and help users understand the link’s purpose. Internal linking helps search engines find important pages.
Security Best Practices
Links can expose your site to security risks. Avoid linking to unsafe or untrusted websites. Use “nofollow” attributes for paid or sponsored links. Always check external links to protect your site visitors from harmful content.
Credit: www.contexteditor.org
Link Accessibility Tips
Making links accessible helps all users navigate your site easily. Proper link accessibility improves usability for people with disabilities. This section covers simple tips to create accessible HTML links.
Descriptive Link Text
Use clear and specific words for your link text. Avoid vague phrases like ”click here” or ”read more.” Describe what users will get after clicking the link. For example, use ”Download the annual report” instead of ”Download.” Descriptive text helps screen readers explain the link’s purpose better.
Keyboard Navigation
Ensure all links can be accessed using a keyboard. People who cannot use a mouse rely on keyboard navigation. Test your links by using the Tab key to move through them. Links should have a visible focus style so users know which link is active. This helps users navigate without confusion.
Screen Reader Support
Screen readers read link text aloud to users with vision loss. Make sure the link text makes sense on its own. Avoid links that depend only on context, like ”here” or ”this page.” Use ARIA labels if extra description is needed. This ensures screen readers provide useful information about the link.
Best Practices For Perfect Hyperlinks
Creating perfect hyperlinks enhances user experience and site navigation. Good links guide readers clearly and quickly. Following best practices helps keep links useful and accessible. This section covers key tips for making effective HTML links.
Consistent Styling
Use the same color and style for all links. Consistent styling helps users recognize clickable text. Avoid too many colors or fonts for links. Underline links or use bold text for clarity. Keep styles simple to improve readability.
Clear Purpose
Make link text descriptive and meaningful. Readers should know where the link leads. Avoid vague phrases like ”click here” or ”read more.” Use specific words related to the linked page. Clear links reduce confusion and increase clicks.
Performance Optimization
Use clean HTML code for faster loading. Avoid unnecessary tags inside links. Minimize the use of large images or scripts in link areas. Use relative URLs for internal links to speed up navigation. Fast links improve user experience and SEO.
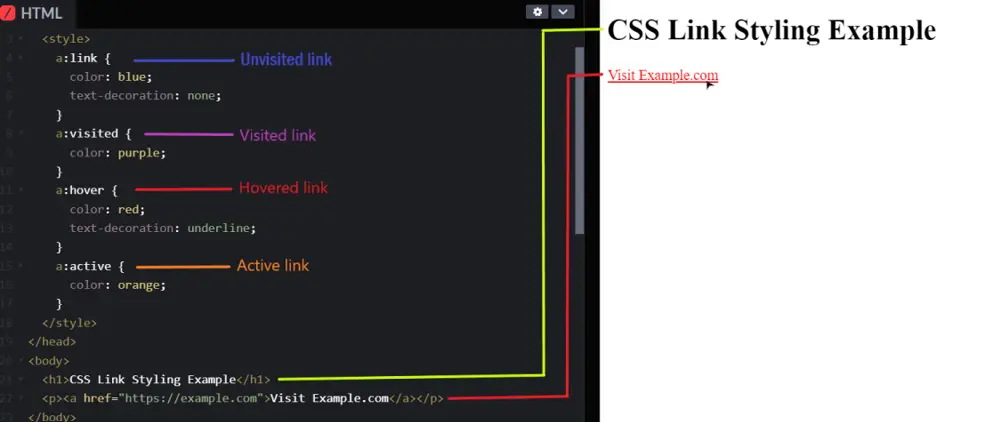
Credit: iqratechnology.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Basic Html Code For A Link?
The basic HTML code for a link uses the tag with the href attribute. Example: Link Text. This creates a clickable link that directs users to the specified URL when clicked.
How Do I Open A Link In A New Tab Using Html?
To open a link in a new tab, add the attribute target=”_blank” to the tag. Example: Link. This makes the browser open the link in a new tab or window.
Can I Add A Title To An Html Link?
Yes, adding a title attribute to the tag provides extra info on hover. Example: Link. This improves accessibility and user experience by showing descriptive text.
How Do I Link To An Email Address In Html?
Use the mailto: protocol in the href attribute. Example: Send Email. Clicking this link opens the user’s default email client to compose a new message.
Conclusion
Creating a link in HTML is simple and useful. It helps users move between web pages quickly. Just use the anchor tag with an href attribute. Remember to add clear text inside the tag. This way, visitors know where the link goes.
Practice writing different links to get comfortable. Soon, linking will feel natural and easy. Keep your code clean and organized. Links connect your website and make it more helpful. Start adding links today and see the difference.

